Detailed descriptions and effective treatments for potato diseases
There are many potato diseases that cause serious crop damage. They arise not only during the growing season, but also during storage. It is possible to correctly determine the cause of the problem and choose the appropriate method of elimination, knowing its characteristic symptoms. The article will tell you about the causes of potato diseases, their symptoms and treatment methods.
The content of the article
Reasons why potatoes can get sick
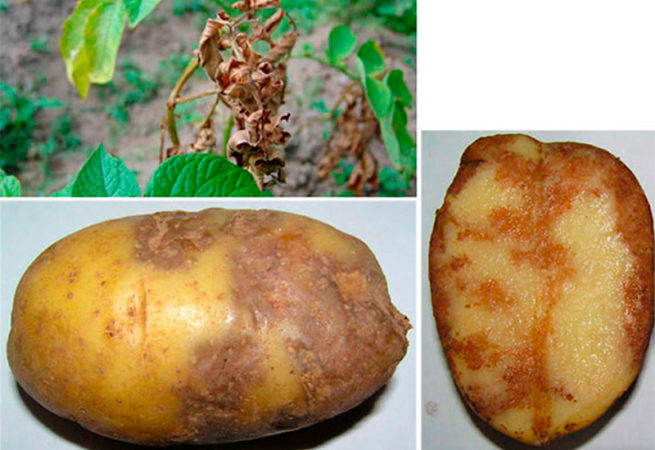

Factors contributing to the emergence of cultural diseases include:
- the use of infected planting material;
- non-compliance with the rules of agricultural technology;
- violation of crop rotation;
- invasion of pests;
- adverse weather conditions;
- the wrong type of soil or the presence of fungus in it.
One of the causes of potato diseases is the planting of a variety that is not suitable for a particular area.
How to distinguish diseases from micronutrient deficiencies and errors in growing and care
Nutrient deficiencies and improper care lead to the development of physiological diseases.
Their difference from infections is as follows:
- absence of a pathogen;
- simultaneous damage to most of the plants growing in the garden;
- the possibility of eliminating the problem by correcting errors in agricultural technology.
During the course of physiological diseases, their signs are observed immediately on all organs of vegetable crops. This can be discoloration, deformation, drying and dieback.
As a result, the plant begins to lag behind in growth. Unlike infections and viruses, this problem rarely leads to death.
Important! On infected plant specimens, aphids almost always appear - a carrier of various fungi and bacteria.
Description of potato diseases with photos and treatment methods
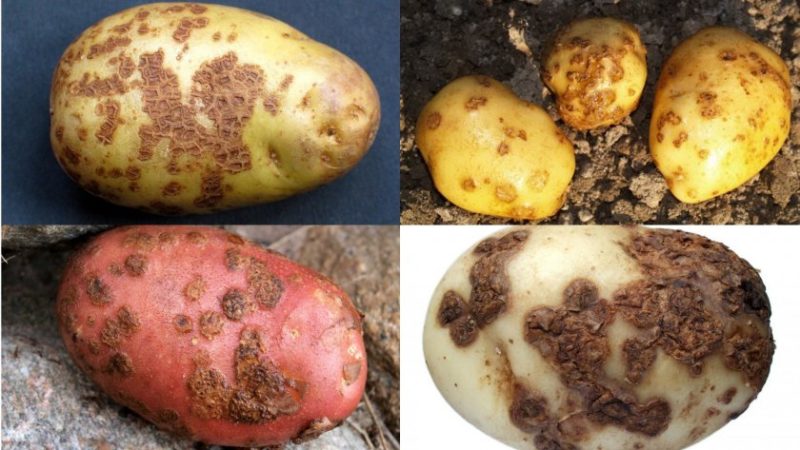

Potato diseases are divided into several groups depending on the nature of the infectious agents:
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- viral.
Each of the groups has its own specificity, requiring specific treatment and prevention.
Important! Knowing the characteristics of diseases allows you to take preventive measures in advance in order to prevent the occurrence of problems.
Let's take a closer look at potato diseases and measures to combat them.
Fungal
These diseases are caused by pathogens and spread by spores.
The source of infection can be working equipment, planting material, soil or the remains of last year's tops. Active reproduction of spores stimulates an increase in temperature and humidity levels, as well as a violation of the rules of agricultural technology.
There are several types of fungal diseases:
- anthracnose;
- late blight;
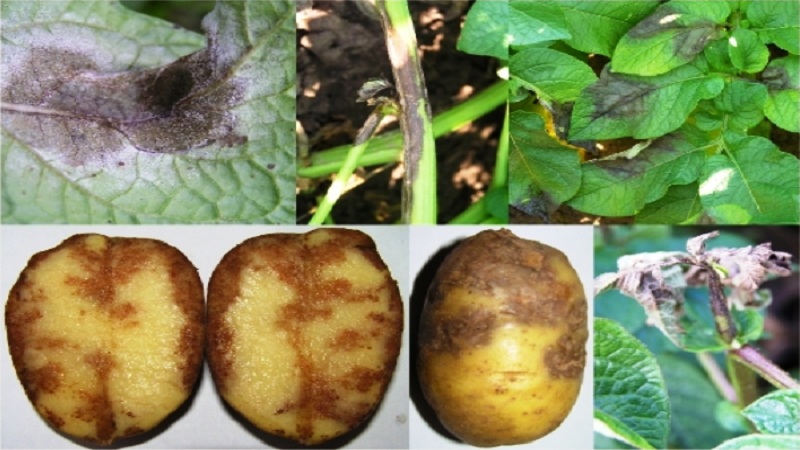 Late blight
Late blight - scab - black, silvery or powdery;
- cancer potatoes;
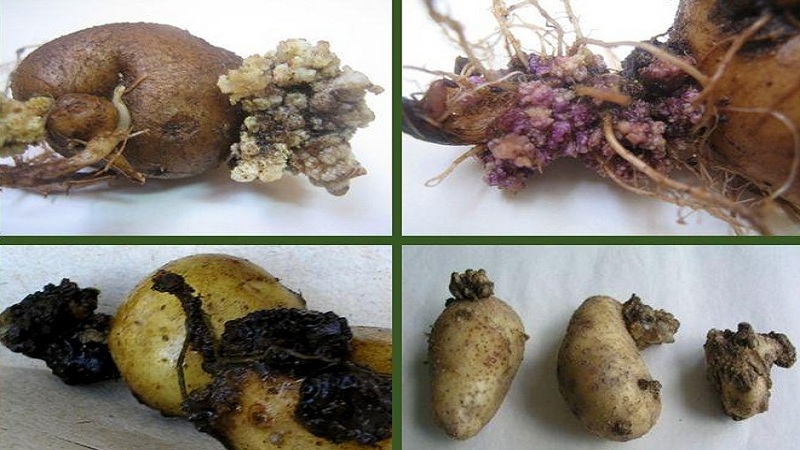 Cancer
Cancer - dry rot;
- alternaria;
- macrosporiosis;
- verticillosis.
Signs of culture defeat:
- the appearance of brown or brown spots at the bottom of the stems;
- rot;
- twisting and wilting of leaf plates;
- the possibility of easy extraction from the soil;
- the formation of white bloom on the leaves;
- the appearance of gray spots and growths on the tubers.
Treatment methods
There are several ways to combat fungal diseases: folk, chemical, biological.
Folk
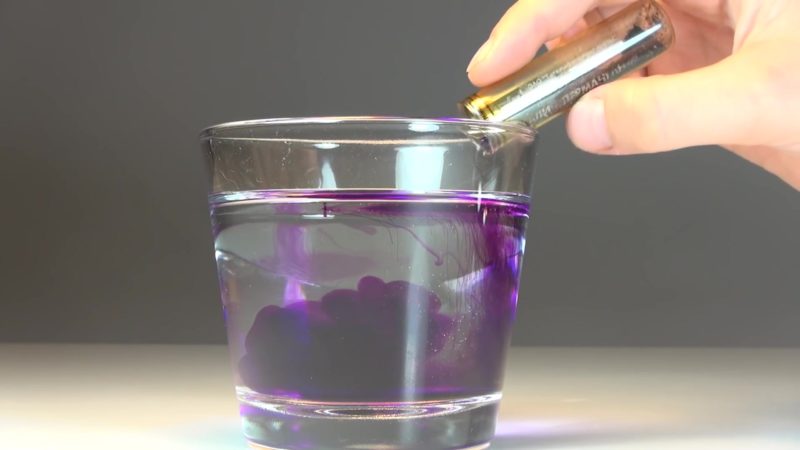

Processing with prepared solutions:
- potassium permanganate - 10 g per 10 liters of water;
- copper sulfate - 2 g per 10 liters;
- 100 g of copper sulfate and 100 g of soda ash, diluted in 10 liters of water - are used during the growing season in the amount of 6 liters per 1 hundred square meters.
Chemical
Use of fungicides:
- "Profit";
- Thanos;
- Novozir;
- "Mancozeb".
During the growing season, the tops are treated with one of the compositions prepared according to the instructions attached by the manufacturer.
Biological
At the beginning of the budding stage, the tops are sprayed with protective preparations, adhering to the following dosages per one hundred square meters:
- Ecosil - 5 ml per 1 liter of water;
- Gibbersib - 0.015 g;
- "Bitoxibacillin" - 30 g;
- "Baktofit" - 50 ml;
- "Fitosporin" - 6 g.
An effective treatment for fungal diseases is drying tubers in the sun for 4-5 hours a day of digging.
Bacterial
The cause of this problem is bacteria that provoke intoxication and death of a vegetable crop. They can be found in nearby weeds or contaminated soil. Bacteriosis often occurs in a latent form.
It is rather difficult to identify them due to their ability to change signs, which is due to a number of reasons:
- weather conditions;
- by the type of pathogen bacteria;
- the degree of defeat.
Bacteriosis often appears on areas of tubers damaged during harvesting and transportation.
Types of bacterial diseases:
- blackleg;
- brown rot;
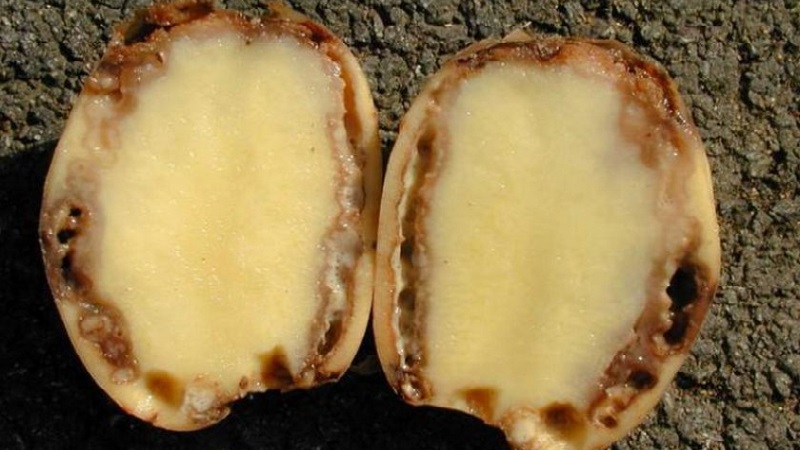
- ring rot;
- mixed internal rot;
- wet rot of tubers.
Signs of defeat:
- blackening of the lower sections of the stems;
- the formation of mucus on the tops of the bushes;
- twisting of leaf plates, their wilting and falling off;
- leaf rot at the surface of the soil;
- decay of stems;
- the appearance of yellow spots on the leaves;
- the appearance of putrefactive spots outside and inside the tubers.
Treatment methods
The risk of developing diseases is significantly reduced with timely disposal of the foliage (mowing, removal from the beds).
Folk
The sequence of preparation of a remedy:
- pour 1 kg of dry wormwood with a little water and boil for 15 minutes;
- for 2 days, insist 1 kg of manure in water, then mix with a decoction of wormwood;
- strain the mixture and add more water to it to make 10 liters;
- add 40 g of crushed laundry soap.
Potatoes are processed from the beginning of budding, the required number of procedures is at least 3 with a break of 14 days. It is permissible to use tobacco broth for spraying.
Chemical
Before planting, the tubers are treated with TMTD (2.4 l / t).
When placed in storage, the crop is sprayed with the Maxim fungicide: for every 10 kg, there are 2 ml of the product diluted in 50 ml of water.
Biological
This method involves the treatment of tubers with the "Planriz" composition. The recommended dosage is 1 liter (0.1%) per 100 kg.
Viral
This group of diseases is considered the most dangerous, since there are no effective methods of combating viral pathologies.
Virus damage occurs when healthy potato bushes and tubers come into contact with sick ones. Insects, especially cicadas and aphids, carry the infection.
The mosaic virus destroys up to 40% of the crop and is divided into 3 types:
- Wrinkled - characterized by the formation of wrinkles on the leaves between the veins. As a result, the foliage gradually dries up, but remains on the bushes. Its color takes on a bronze tint. For the purpose of prophylaxis, the culture is treated with "Ridomil" and "Ditan" means.
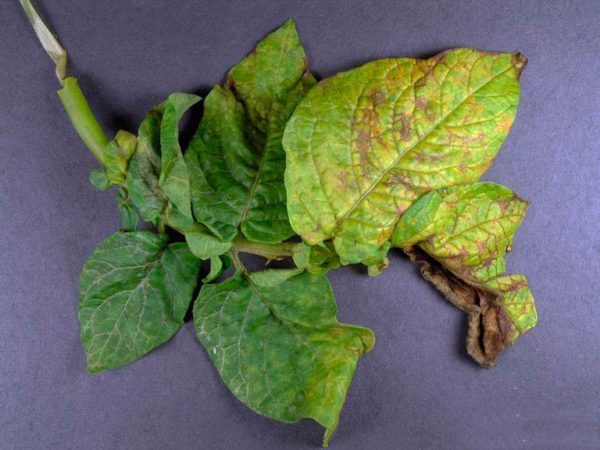

- Striped - manifests itself in the budding phase. Symptoms are the formation of yellow-green stripes on the front side of the leaf plates and brown ones on the inside. The stems of the plant become thinner and break under their own weight. As a preventive measure, the bushes are sprayed with Bravo and Shirlan preparations.
- Speckled - is expressed by the appearance of pale green spots on the leaves. For the prevention of this form of mosaic use "Quadris" and "Revus".
Potatoes are processed in order to prevent viral diseases several times during one season, observing the interval between procedures (18 days).
The leaf curl virus is usually carried by the wind and can also be infected through the soil. In this case, the leaves acquire a yellowish or pink hue, become fragile and curl up into a tube.
Important! Since this disease does not respond to treatment, the affected bushes must be destroyed.
Potato post-wilt is usually observed in hot climates. This virus is spread by infected perennial weeds.
Signs of culture defeat:
- curliness and elongation of leaves;
- dying off of the root system;
- stunting.
Due to the rapid spread of the disease, the disease can destroy large areas of planting in a short time. There are no medications for stolbur.
In order to prevent the disease, a number of measures are recommended:
- strict adherence to the rules of crop rotation;
- use of high-quality planting material;
- timely weeding, loosening, weed control and other rules of agricultural technology.
Necrosis is a dangerous virus that mostly develops in tubers and is almost invisible on the top of bushes. This is one of the reasons why potatoes turn black on the inside. As a result, a substantial part of the crop rots and dies. You can reduce the risk of this problem by following the rules of crop rotation and using healthy material for planting.
When the Gothic virus is infected, the appearance of the potatoes changes, but the taste remains the same. Tubers lose 20% of starch and stretch, while the number of eyes increases. Leaves and tubers take on an ink shade. The main carriers of the Gothic are aphids, grasshoppers, bugs and Colorado beetles.
Preventive measures against potato diseases
Prevention of the development of diseases involves:

- Treatment of seed material before planting with one of the preparations: "Confugo", "Maxim", "Prestige", "Fitosporin-M" or copper sulfate.
- Use of varieties resistant to infections.
- Periodic rotation of crops in one area. Planting is carried out taking into account compatibility, it is desirable that the vegetable crops belong to different families, since most often "relatives" are susceptible to diseases.
- Thorough preparation of the site before planting, standardized fertilization.
It is not recommended to grow potatoes on the same plot for more than one year. Re-planting is only allowed after 4-6 years.
Ideal precursors for potatoes:
- winter cereals;
- corn;
- legumes and cereals;
- beet;
- perennial herbs.
Tips and tricks from experienced gardeners
To increase the resistance of potatoes to various diseases and the effectiveness of treatment, experienced gardeners recommend:
- Regularly apply potassium-phosphorus fertilizers, nitrogen and boric acid to the soil.
- A month before planting, expose the planting material under diffused light: the duration of the procedure is 12 days, the appropriate temperature is 22 ° C. Greened tubers will become resistant to pathogens.
- If ring rot is found, destroy the affected bush, and pour 1 liter of copper sulfate diluted with water (100 g per 1 liter) into the hole.
- Before planting, treat the soil with a solution containing copper, which will prevent the occurrence of fungal diseases.
- During the flowering period, use wood ash or potassium sulfate as top dressing. This increases the plant's resistance not only to diseases, but also to possible frosts.
Conclusion
It is much easier to prevent diseases of potato tubers than to cure them even at the very early stage.Therefore, the cultivation of this culture requires strict adherence to the rules of agricultural technology.
Planting material also needs special attention: its treatment with special preparations before planting and storage will relieve bacteria and spores, and at the same time increase immunity.